Welcome to the AI Safety Newsletter by the Center for AI Safety. We discuss developments in AI and AI safety. No technical background required.
In this edition we discuss the new AI Dashboard, recent frontier models from Google and Anthropic, and a revived push to preempt state AI regulations.
Listen to the AI Safety Newsletter for free on Spotify or Apple Podcasts.
This Giving Tuesday, CAIS is raising support to scale our research and public education around AI safety. If you’ve found value in our newsletter or other work and you’re interested in helping to advance these efforts, you can contribute to our Giving Tuesday campaign.
Donate hereCAIS Releases the AI Dashboard for Frontier Performance
CAIS launched its AI Dashboard, which evaluates frontier AI systems on capability and safety benchmarks. The dashboard also tracks the industry’s overall progression toward broader milestones such as AGI, automation of remote labor, and full self-driving.
How the dashboard works. The AI Dashboard features three leaderboards—one for text, one for vision, and one for risks—where frontier models are ranked according to their average score across a battery of benchmarks. Because CAIS evaluates models directly across a wide range of tasks, the dashboard provides apples-to-apples comparisons of how different frontier models perform on the same set of evaluations and safety-relevant behaviors.
Ranking frontier models for safety. The AI Dashboard’s Risk Index offers a view of how today’s frontier models perform across six tests for high-risk behaviors. It then averages the scores and ranks them on a 0–100 scale (lower is safer). Here are the benchmarks and hazardous behaviors they measure:
- The refusal set of the Virology Capabilities Test measures a model’s usefulness at answering dual-use biology questions.
- The Agent Red Teaming benchmark measures a model’s robustness against jailbreaking.
- Humanity’s Last Exam - Miscalibration tests overconfidence on difficult academic questions by comparing its stated confidence to its actual accuracy.
- MASK tests how easily models can be pressured into deliberately giving false answers.
- Machiavelli evaluates whether an AI engages in strategic deception, including planning, exploiting, or deceiving in text-based scenarios.
- TextQuests Harm assesses how likely an AI is to take intentionally harmful actions in text-based adventure games.
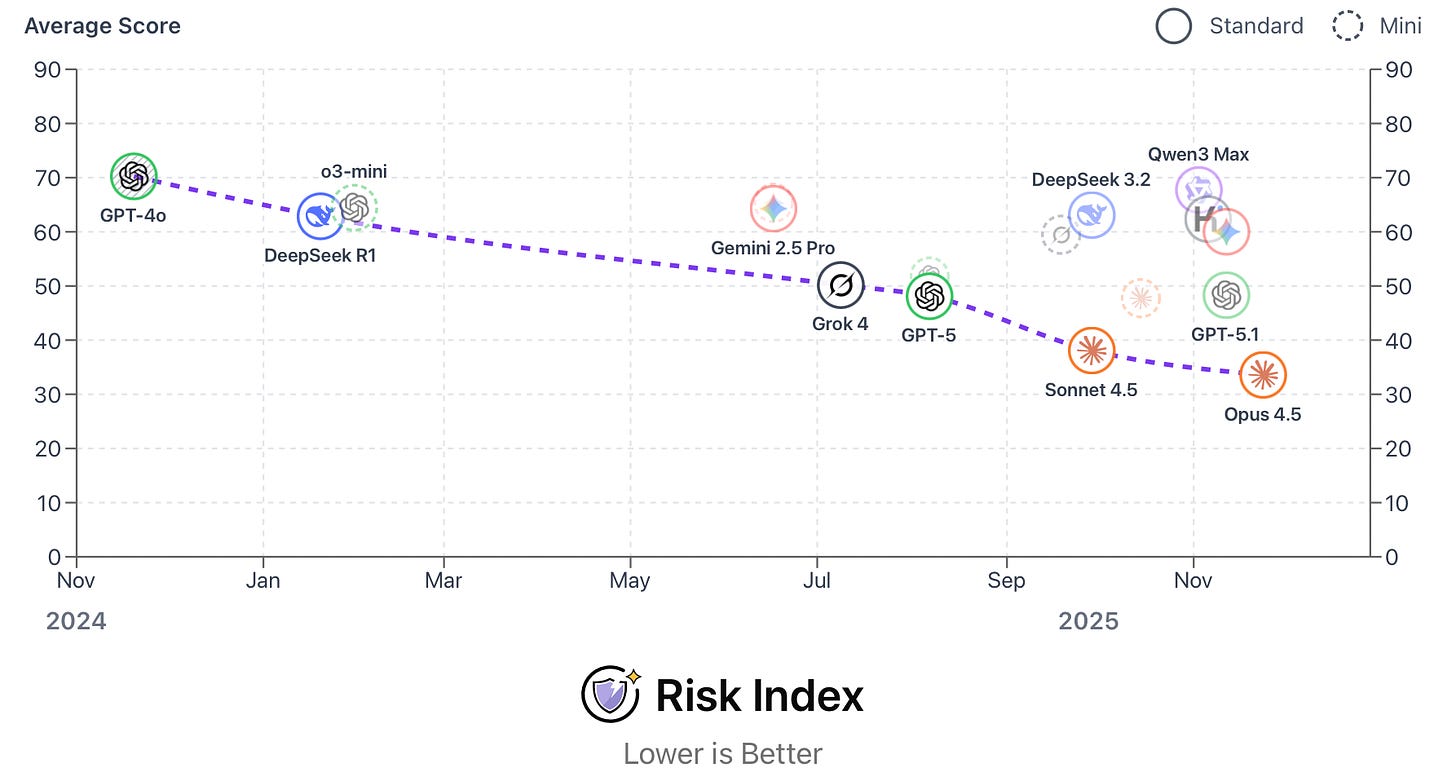
Across these tests, Anthropic’s recently-released Claude Opus 4.5 is currently the safest frontier model, with an average score of 33.6.
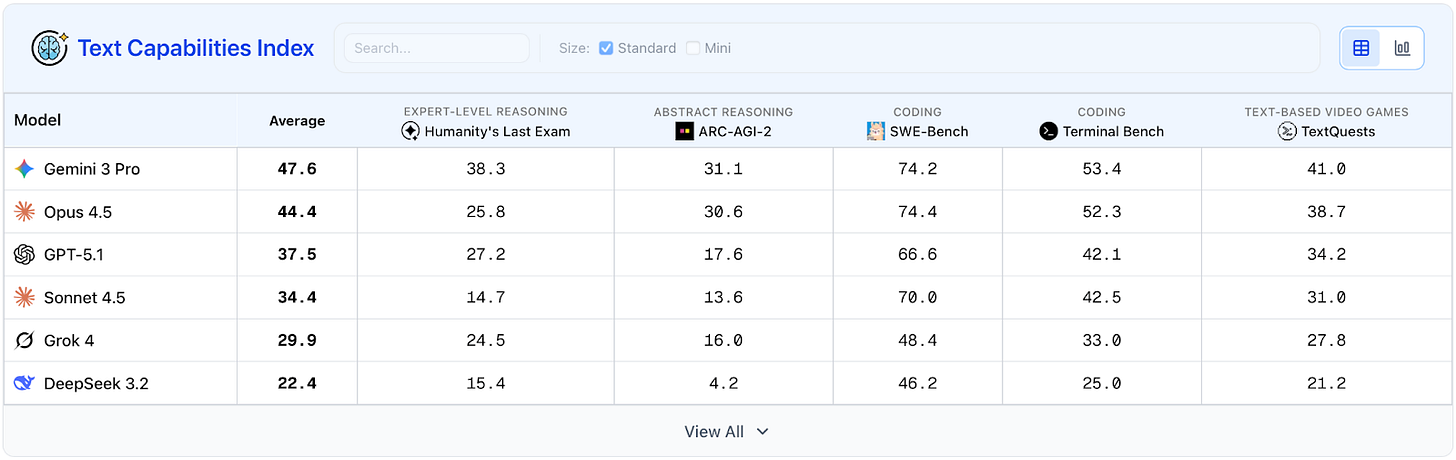
Ranking the frontier systems’ technical capabilities. The Dashboard’s Text and Vision Capabilities Indexes each test systems across five benchmarks. The text-based evaluations test systems on coding, systems administration, expert and abstract reasoning, and performance in text-based adventure games. The vision evaluations measure embodied reasoning, navigation, mental visualization, intuitive physics, and puzzle solving.
Measuring progress toward broad automation. The AI Dashboard also monitors progress toward three key automation milestones. It measures the industry’s overall advancement toward AGI using CAIS’s recently published definition. It evaluates progress on fully automating remote work through CAIS’s Remote Labor Index, which tests AI agents’ ability to complete paid, remote freelance projects across 23 job categories. Finally, it tracks development of autonomous vehicle safety using data from a community-run project documenting Tesla’s Full Self Driving disengagements.
Politicians Revive Push for Moratorium on State AI Laws
A leaked draft executive order from a member of the Trump administration details a plan to prevent U.S. states from regulating artificial intelligence. Meanwhile, some congressional lawmakers are trying to pass a similar law by including it in a sweeping defense bill.
The executive order would empower federal agencies to preempt state AI laws. The draft executive order would require federal agencies to identify state AI regulations deemed burdensome and push states to avoid enacting them.
The draft order directed federal agencies to take the following actions:
- The U.S. Department of Justice to establish an AI Litigation Task Force tasked with suing states whose AI laws are deemed to interfere with interstate commerce or conflict with federal authority.
- The U.S. Department of Commerce to withhold federal broadband or infrastructure funding from states found to have onerous preexisting AI laws.
- The Federal Trade Commission to develop nationwide rules that would preempt state laws that conflicted with federal regulations.
- The Federal Communications Commission to examine whether state AI laws that “require alterations to the truthful outputs of AI models” are prohibited under existing laws.
It also ordered the creation of a nationwide, lighter-touch regulatory framework for AI, though it lacked specifics.
Congress revives its own efforts for a moratorium. House leaders are considering using the annual defense spending bill as a vehicle for a moratorium on state AI regulations. The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA), a must-pass measure, is often used to advance other policy priorities. Specifics of the proposed language remain unclear. An earlier attempt called for a 10-year ban, later shortened to five years and limited to states seeking federal broadband funds. It was ultimately defeated by a bipartisan coalition of senators.
57% of American voters oppose inserting preemption into the NDAA. The same poll, from YouGov and the Institute for Family Studies, found that 19% supported the measure and 24% were unsure. Citing voter concerns, a coalition of over 200 lawmakers urged congressional leaders to drop the provision. Due to stiff opposition—and the fact that its controversial nature would likely delay the must-pass NDAA—Axios has characterized this effort as a long shot. Voting is expected in early December.
Gemini 3 Pro and Claude Opus 4.5 Arrive
Google’s Gemini 3 Pro is now the strongest frontier system on nearly all general-purpose capability benchmarks—but trails other frontier systems in safety. Anthropic’s new Claude Opus 4.5 is close behind in capabilities but topped the frontier rankings in safety.
Gemini 3 Pro tops text and vision leaderboards. In independent evaluations performed by CAIS and posted on the new AI Dashboard, Gemini 3 Pro achieved state-of-the-art scores on both text and vision benchmarks. In some tests, it scored double-digit improvements over models released just weeks earlier.
Claude Opus 4.5, released a week after Gemini 3 Pro, averaged second place on both the text and vision capability indexes, and beat Gemini 3 Pro by 0.2 points at SWE-Bench.
What’s new in Gemini 3 Pro and Claude Opus 4.5. Google has positioned Gemini 3 Pro as having improved reasoning, broader agent capabilities, and expanded control settings. The company also released a new coding agent, Antigravity, based on the model. Google also notes that an enhanced reasoning version — Gemini 3 Deep Think — is still under safety testing before full release.
Anthropic highlighted Claude Opus 4.5’s productivity‑focused enhancements along with its high coding scores. New features include a larger context window and a new “effort” parameter that allows developers to adjust their speed, cost, and depth of processing.
There is significant safety variation across frontier models. Claude Opus 4.5 scored lowest on the AI Dashboard’s risk capabilities index, making it the current safest frontier model. Anthropic’s internal safety audit noted that Claude Opus 4.5 was measurably safer than earlier models, but somewhat vulnerable to certain jailbreaking techniques. They noted it showed a tendency toward evaluation awareness and dishonesty.
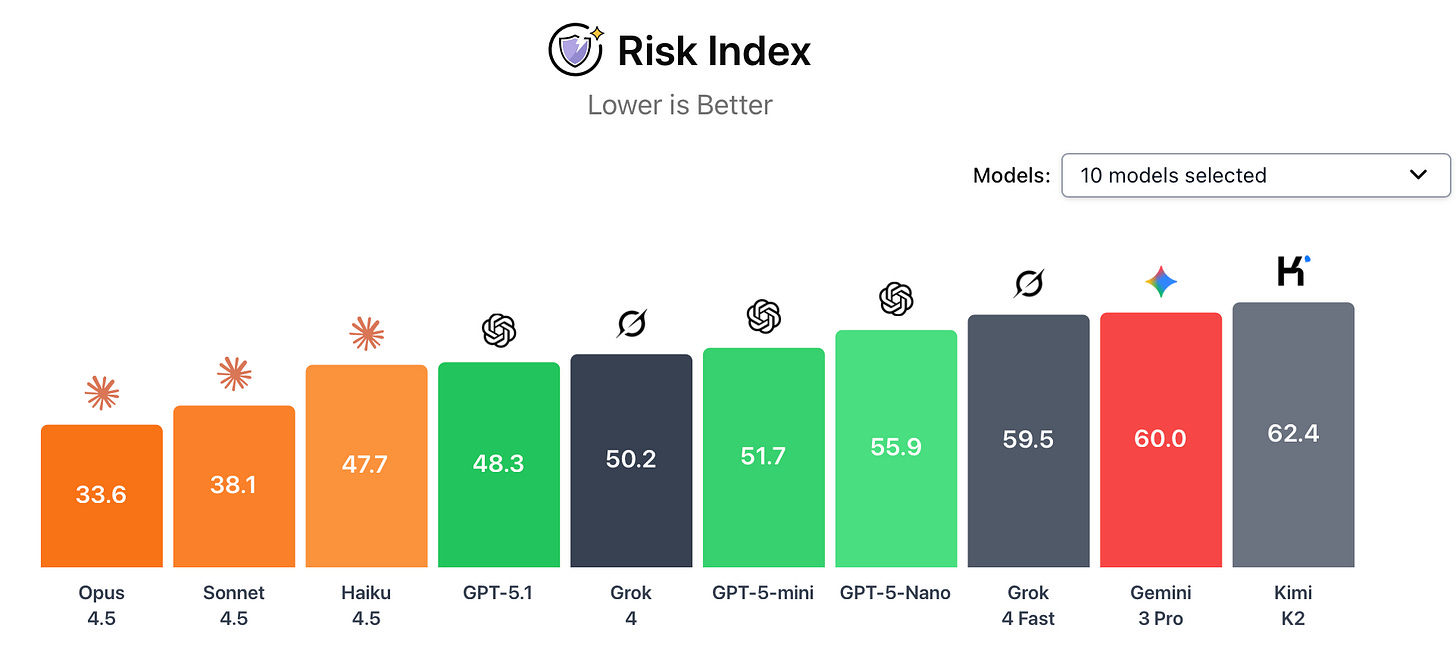
Gemini 3 Pro ranked ninth on the risk capabilities index, underperforming relative to other recent frontier models. Gemini 3 Pro’s safety report acknowledges that the model exhibits risky behaviors in certain capabilities (for example, cybersecurity) and says extra mitigations have been deployed as part of its “Frontier Safety” framework. Internal evaluations also showed that the model can manipulate users.
Listen to the AI Safety Newsletter for free on Spotify or Apple Podcasts.
Subscribe to receive future versions.
In Other News
Government
- Former Representatives Chris Stewart (R‑UT) and Brad Carson (D‑OK) announced a new nonpartisan organization and two bipartisan super PACs, aiming to raise $50 million to promote AI safeguards and fund candidates committed to AI safety.
- Leading the Future, a pro-AI super PAC, announced it will fund a campaign against Alex Bores, author of the RAISE Act.
- The European Commission proposed delaying its rules on “high-risk” AI systems until 2027, after facing pushback from the U.S. and the tech industry.
- The Department of Energy launched the Genesis Mission: a program aiming to double American research productivity within a decade by linking the country’s leading supercomputers, AI systems, and scientific infrastructure into a unified discovery platform.
Industry
- OpenAI CEO Sam Altman clarified that he “does not have or want government guarantees for OpenAI data centers” following his CFO’s proposal for a U.S. government backstop.
- Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang told the Financial Times that “China is going to win the AI race.”
- Yann LeCun, longtime head of Facebook AI Research, is reportedly leaving Meta to start a new AI company pursuing human-level intelligence through alternative methods to LLMs.
- Larry Summers resigned from the OpenAI board following revelations of his close personal relationship with Jeffrey Epstein.
- Waymo began offering taxi rides that take the freeway in Los Angeles, Phoenix, and San Francisco.
Civil Society
- RAND researchers explored technical options for countering rogue AI systems, including high-altitude electromagnetic pulses, a global internet shutdown, and training specialized models to hunt down rogue AIs.
- A new paper outlines 16 unsolved problems in ensuring safety in open-source AI models, which attackers can freely modify.
- Anthropic reported that cybercriminals used Claude Code to automate between 80% and 90% of tasks within real-world cyberattack operations.
- AI startup Edison Scientific announced Kosmos, a model trained to ingest scientific research, generate hypotheses, analyze data, and produce reports.
- Researchers found that turning harmful prompts into poetry can act as a universal jailbreak, dramatically boosting the success of attacks across leading AI models.
See also: CAIS’ X account, our paper on superintelligence strategy, our AI safety course, and AI Frontiers, a platform for expert commentary and analysis.
